Working principle
The inverting amplifier configuration produces an output voltage equal to its input voltage multiplied by a negative ratio of its two resistors:
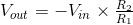
Formula derivation
Since any ideal op-amp tries to keep its two terminals at an equal voltage, the inverting input of the op-amp (V-) is at the same potential as the non-inverting terminal (V+) and, thus, forms a virtual ground at its node: V- = V+ = 0.
Since the op-amp’s input terminals (V+ and V-) have an infinite input impedance, there is no current flowing into them. Instead, all of the current flowing through R1 also flows through R2:
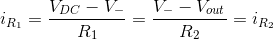
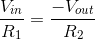
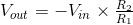
Experiments
- Vary the input voltage and resistor values and observe the change at the output.
- Change the input voltage to a negative value and verify that the output voltage is now positive (inverted).
- Make R1 and R2 equal to create an inverting buffer. What is the output voltage now in terms of the input voltage?
